I was doing a bit of background reading and came across an interesting paper about mutating normal bacteria into cancer-fighting bacteria. The paper centers around a single gene called inv (short for invasin) that can give an otherwise mild-mannered noninfectious bacteria the ability to invade cells.
Now this might seem like a pretty bad idea since there are probably enough infectious bacteria in the world already but this was only the first step of the research. Anderson and colleagues attached inv to a genetic switch (normally used for bacterial metabolism control) that turns on when arabinose (a type of sugar) is present. Unfortunately this switch was a little leaky. So even bacteria without arabinose were still infectious. Not ones to let that stop them, the researchers took out the ribosome (protein-making organelle) binding region of the gene, randomly mutated it and tested to find bacteria that were off by default but still able to turn on.
Once they got that working, they decided to attach a sensor to the infective gene. Bacteria often do things like switch metabolisms when they run out of oxygen. The researchers picked one of the bacteria genes that turns on when oxygen is low and replaced the arabinose switch from the previous bit with the oxygen sensing switch from this gene. Again the switch was leaky and they had to mutate it so it stayed off by default. Once that was done they had a bacteria that was only invasive in anaerobic environments. That’s pretty cool because tumors are often anaerobic (since they’re big lumps of fast growing dense tissue).
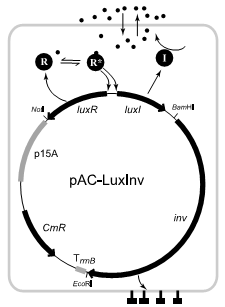
To go even further, the researchers tried to create bacteria that only turn on when there are many bacteria in one location. This will be useful because tumors often have higher concentrations of bacteria due to leaking nutrients and poor immune response. By creating a switch that only turns on when a bunch of bacteria are present, the bacteria can be further targeted to cancerous cells. To do this they used a gene from an ocean-dwelling bacteria that only turns on when many bacteria are present (the ocean bacteria uses the gene to detect when it has reached the light organ of squid). It seems odd that bacteria can communicate but it comes down to a simple mechanism made up of two genes. One gene encodes an enzyme that makes a chemical, called AI-1, that easily disperses in and out of the cell membrane. The second encodes a gene activator that is turned on by high concentrations of AI-1. When there are many bacteria, the environment becomes rich in AI-1 and the gene activator turns on even more production of AI-1 and gene activators. This positive feedback causes creates a sensitive switch that switches quickly from all off to all on when bacterial concentration crosses a certain level. By linking these genes to the infectious inv gene, the researchers created a bacteria that was only infectious when in high concentrations.
So now we have bacteria that might be able to selectively infect tumor cells. By combining this selective invasiveness with cell killing or immune response activating mechanisms, bacteria could become helpful tools for treating cancer (although there is still a pretty long way to go). The paper makes it look easy but that must have taken a good bit of work to get it all working so nicely. They ended up using DNA from three different bacteria species and many different bacterial systems. It’s always really cool to see how scientists can take DNA “parts” and combine them together to create new and useful functions and even edit the DNA directly when the parts don’t fit correctly.
I guess the next step in the research is to figure out how to get a bacteria to sense both an anaerobic and a high density environment. This might be a bit tricky since the two sensors would have to interact but I see some of the same researchers also have a paper on creating bacterial AND gates so I’ll have to give that one a read too.
Reference
Anderson, J., Clarke, E., Arkin, A., Voigt, C. (2006). Environmentally Controlled Invasion of Cancer Cells by Engineered Bacteria. Journal of Molecular Biology, 355(4), 619-627. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.10.076


 It looks like I’m the next host of the biology blog carnival
It looks like I’m the next host of the biology blog carnival